들어가기 전
『자바 웹 프로그래밍 Next Step』 4장에 나와있는 웹 서버 요구사항들을 구현해보았다. 구현하기 전, 스스로 아래와 같은 사항을 다짐하고 진행해봤다.
- 최대한 책에 나온 힌트를 보지 않고 해결해보자.
- 반드시 테스트 코드를 작성하자.
- 빠르게 구현하는 것 보다 중요한건 코드 한 줄 한 줄의 의미를 제대로 아는 것.
- 의식적으로 리팩토링 연습을 하자.
처음엔 html 페이지만 클라이언트로 전달하는 요구사항이었는데 나중엔 Map을 임시 DB로 활용하여 회원가입하는 것까지 하게되었다. 다 만들어보고 나니 엄밀히 말하면 매우 간단한 ‘WAS’라고 할 수 있을 것 같다.
연속으로 시간을 할애하진 못했지만, 다 합치면 대략 2주 정도 걸린 것 같다.
요구사항 별 구현
요구사항 별로 구현을 하면서 몰랐던 내용들과 배운 내용, 구현 사항 등을 기록해보았다.
요구사항 1
http://localhost:8080/index.html로 접속했을 때 webapp 디렉토리의 index.html 파일을 읽어 클라이언트에 응답한다.
구현하기 전 들었던 생각들
- index.html 파일을 어떤식으로 클라이언트에 넘겨줘야할까 ?
- index.html 파일 읽어서 byte 형태로 만들어준 뒤 DataOutputStream을 통해 response 넘기면 되지 않을까.. ?
- http://localhost:8080/index.html 라는 요청왔을 때 ‘/’ 이후의 파일명을 어떻게 가져오지 ?
구현
베이스 코드에 있던 ‘RequestHandler’ 클래스 내부에 구현했다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
// 클라이언트가 요청한 html 파일 이름 가져온다
private String getRequestHtmlName(InputStream in) throws IOException {
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in));
String requestInfo = bufferedReader.readLine();
if(!requestInfo.contains(".html")) {
return null;
}
String htmlPage = requestInfo.split(" ")[1];
return htmlPage.substring(1); // 맨 앞에 '/' 지우기 위함
}
// http response를 위해 파일을 byte로 변환 (절대경로 ver)
private byte[] convertHtmlToByte(String fileName) throws IOException {
String rootPath = System.getProperty("user.dir");
String filePath = rootPath + "/webapp/" + fileName;
File file = new File(filePath);
return Files.readAllBytes(file.toPath());
}
// http response를 위해 파일을 byte로 변환 (상대경로 ver)
private byte[] convertHtmlToByte(String fileName) throws IOException {
String filePath = "./webapp/" + fileName;
File file = new File(filePath);
return Files.readAllBytes(file.toPath());
}
구현하면서 알게된 것들
- 브라우저에서 넘어오는 request가 어떤식으로 구성되어있는지
connection.getInputStream()을 디버거로 찍었는데 요청에 대한 문자열 정보가 보이지 않는다. (connection은 Socket 객체)InputStream은 바이트 단위로 숫자를 저장하기 때문에 원하는 값 볼 수 없었던 것.(참고)BufferdReader,InputStreamReader를 활용하여 byte array인InputStream을 읽어보니 요청의 맨 첫번째 줄에 html 파일에 관련된 정보가 있다.
- 상대경로를 사용할 경우,
./(현재 위치)는 bin, src 폴더를 포함하는 해당 자바 프로젝트 폴더의 위치이다.
요구사항 2
GET 방식으로 회원가입하기
구현하기 전 들었던 생각들
- 요구사항1 에서 구현한 메서드를 개선해야 할 것 같다.
- js, css 파일에 대한 요청도 response로 넘겨줘야 하기 때문에
getRequestHtmlName(),convertHtmlToByte()라는 메서드명을 좀 더 추상적으로 변경하여 html 파일 이외에도 처리가 가능하도록 만들어 보자. - client 관련 파일 디렉토리 최상위 폴더인 “webapp”도 변수에 추가하지 말고 클래스 변수로 선언하고 final로 상수화 하는게 나을 것 같다.
- js, css 파일에 대한 요청도 response로 넘겨줘야 하기 때문에
- 본격적으로 회원가입에 요청에 대해 생각해보면, 지금까지 했던 페이지 응답과는 달리 회원가입 이라는 ‘비즈니스 로직’을 수행해야 한다.
- 따라서, 비즈니스 로직 수행을 담당하는 ‘무언가’를 만들어야 할 것 같다.
- 또한, RequestHandler에서 현재는 페이지 응답에 관련된 것만 수행하는데 다양한 request를 적절하게 처리할 수 있도록 변경해야 할 것 같다.
- 정적 자원 요청, 비즈니스 로직 요청 등 각기 다른 요청을 어떻게 구분해야 할까 ?
- 비즈니스 로직을 요구하는 요청을 처리할 실제 로직에 해당 요청을 어떻게 맵핑시키면 좋을까 ?
- 사용자 요청과 해당 요청을 처리하는데 필요한 메서드를 맵핑시켜주는 역할을 하는
LogicMapper생성. - RequestHandler 내에 코드를 추가해서 할 수도 있겠지만, 그렇게 되면 책임이 많아지기 때문에 코드가 점점 복잡해질 것이다.
- 따라서, RequestHandler의 책임을 ‘클라이언트의 요청을 받아들이고 어떤 요청인지 판단 하는 것’으로 한정하는게 좋을 것 같다고 생각했다.
- 사용자 요청과 해당 요청을 처리하는데 필요한 메서드를 맵핑시켜주는 역할을 하는
구현
요청의 타입을 정적 자원(html, css, js 등) 요청과 비즈니스 로직 요청 두 개로 나눠보았다. 일단 아래처럼 구현해봤는데 이렇게 하드코딩으로 분기시키면 변화에 유연하게 대응하기도 어렵고 생각지 못한 케이스도 있을 것 같다. 어떻게 하는게 좋을지 고민해보고 추후에 책도 참고해보자
1
2
3
4
public enum RequestType {
REQUEST_STATIC_RESOURCE,
REQUEST_BUSINESS_LOGIC
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
private RequestType getRequestType(HttpRequest httpRequest) {
String httpMethod = httpRequest.getHttpMethod();
String requestUrl = httpRequest.getRequestUrl();
switch (HttpMethod.valueOf(httpMethod)) {
case GET:
if(requestUrl.contains("?")) {
return RequestType.REQUEST_BUSINESS_LOGIC;
} else if(requestUrl.equals("/") || requestUrl.contains(".")) {
return RequestType.REQUEST_FILE;
} else {
return RequestType.REQUEST_BUSINESS_LOGIC;
}
case POST:
break;
}
return null;
}
비즈니스 로직 맵핑을 위해 일단 아래와 같이 구현했는데, 리플렉션을 마구 썼다. 이 방법 말고는 없을까 ? 사실, executeMethodWithParamsForGetRequest에서 파라미터 맵핑하는 부분도 파라미터 객체에 기본 생성자가 없으면
paramClass.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance()이 부분에서 에러 난다. 그리고 LogicMapper가 최초 한 번만 생성되는 것도 보장되어야 하는 등 아직 미흡한 부분이 많다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
public class LogicMapper {
// 실행할 비즈니스 로직에 대한 정보
static class Execution <T> {
private T targetInstance; // 실행될 비즈니스 로직 객체
private Class logicClass; // 실행될 비즈니스 로직 클래스
private String methodName; // 실행될 메서드 명
private Class paramClass; // 파라미터 클래스
public Execution(T targetInstance, Class logicClass, String methodName) {
this.targetInstance = targetInstance;
this.logicClass = logicClass;
this.methodName = methodName;
}
public Execution(T targetInstance, Class logicClass, String methodName, Class paramClass) {
this.targetInstance = targetInstance;
this.logicClass = logicClass;
this.methodName = methodName;
this.paramClass = paramClass;
}
public T getTargetInstance() {
return targetInstance;
}
public Class getLogicClass() {
return logicClass;
}
public String getMethodName() {
return methodName;
}
public Class getParamClass() {
return paramClass;
}
}
private static Map<String, Execution> getMappingUrl = new HashMap<>();
static {
initGetRequest();
}
// 요청에 따른 실행 맵핑
private static void initGetRequest() {
getMappingUrl.put("/user/create", new Execution(UserLogic.getInstance(), UserLogic.class, "signup", User.class));
}
// 비즈니스 로직 실행되도록
public byte[] doRequestLogic(HttpRequest httpRequest) throws Exception {
HttpMethod httpMethod = HttpMethod.valueOf(httpRequest.getHttpMethod());
String requestUrl = httpRequest.getRequestUrl();
byte[] response = {};
switch (httpMethod) {
case GET:
response = requestUrl.contains("?") ? executeMethodWithParamsForGetRequest(requestUrl) : executeMethodWithoutParamsForGetRequest(requestUrl);
break;
}
return response;
}
// 요청에 파라미터 있는 경우
public byte[] executeMethodWithParamsForGetRequest(String requestUrl) throws Exception {
String[] info = requestUrl.split("\\?");
String url = info[0];
Map<String, String> params = HttpRequestUtils.parseQueryString(info[1]);
Execution execution = Optional.ofNullable(getMappingUrl.get(url)).orElseThrow(NoSuchMethodError::new);
Class paramClass = execution.getParamClass();
Object instance = paramClass.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
for(String key : params.keySet()) {
Optional.ofNullable(paramClass.getDeclaredField(key)).ifPresent((field) -> {
field.setAccessible(true);
try {
field.set(instance, params.get(key));
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
execution.getLogicClass().getMethod(execution.getMethodName(), execution.getParamClass()).invoke(execution.getTargetInstance(), instance);
return "SUCCESS".getBytes();
}
// 요청에 파라미터 없는 경우
public byte[] executeMethodWithoutParamsForGetRequest(String requestUrl) throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
Execution execution = Optional.ofNullable(getMappingUrl.get(requestUrl)).orElseThrow(NoSuchMethodError::new);
execution.getLogicClass().getMethod(execution.getMethodName(), execution.getParamClass()).invoke(execution.getTargetInstance());
return "SUCCESS".getBytes();
}
}
구현하면서 알게된 것들
- 리플렉션 사용해서
대상클래스.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance()실행시 대상 클래스에 기본 생성자 없으면 에러 난다.
요구사항 3
POST 방식으로 회원가입하기
구현하기 전 들었던 생각들
- POST 방식으로 넘어오는 (body에 담겨있는)파라미터는 어떻게 받지 ?
구현
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
if(httpMethod.equals("POST")) {
int contentLen = 0;
for(String line = bufferedReader.readLine(); (!line.isEmpty() && line!=null); line=bufferedReader.readLine()) {
if(line.contains("Content-Length")) {
String[] info = line.split(":");
contentLen = Integer.parseInt(info[1].trim());
break;
}
}
if (contentLen > 0) {
char[] body = new char[contentLen];
bufferedReader.read(body);
String params = new String(body);
}
}
구현하면서 알게된 것들
- POST 방식의 경우 bufferedReader의
readLine()사용하게 되면 http header는 읽지만 body는 읽어오지 못한다.- 원인을 찾아보니 header의 마지막 부분(“”)
readLine()하는 부분에서 계속 hanging 되어있다. - hanging 되는 이유는 request header 마지막 라인이 공백인데
readLine()의 경우 line의 끝에 개행 문자가 없는 경우, 값이 올 때 까지 계속 기다린다고 한다. - 따라서, 공백인 경우를 체크하는 로직이 필요하고, Content-Length를 구해서 그 크기만큼 나머지를
read()하면 된다. readLine()대신read()를 사용하는 이유는, body로 넘어오는 파라미터 또한 끝에 개행문자가 없기 때문에readLine()사용시 대기상태에 빠진다.
- 원인을 찾아보니 header의 마지막 부분(“”)
- http request 포맷
1 2 3 4 5 6
Request-Line *(( general-header | request-header | entity-header ) CRLF) CRLF [ message-body ]
요구사항 4
회원가입을 완료하면 /index.html 페이지로 이동한다. url 또한 user/create가 아닌 /index.html로 변해야 한다.
구현하기 전 들었던 생각들
- 회원가입 후 index.html을 클라이언트로 넘겨주면 페이지는 뜨겠지만 url은 user/create가 그대로 남아있을 것이다.
- 회원가입 후 클라이언트가 index.html을 요청하도록 하려면 어떻게 해야할까 ?
- 비즈니스 로직 수행하는 메서드의 다양한 타입의 리턴값을 LogicMapper에 추상화 시킨 두 개의 메서드
executeMethodWithParams(),executeMethodWithoutParams()에서 어떻게 받아서 처리해야할까?
구현
먼저 웹 서버의 관점에서 생각해봤을때, 웹 서버에서 클라이언트로 응답하는 형태는 크게 ‘html 페이지 / 데이터(json 등)’ 이라고 생각했다. 따라서, 클라이언트의 요청에 대해 적절한 응답을 하기 위해 필요한 것은 위에서 정의한 ‘응답의 형태’와 ‘실제 데이터’ 두 가지라고 생각하여 이를 나타내는
ExecutionResult클래스를 만들었다. 이에 따라 기존에 정의된executeMethodWithParams(),executeMethodWithoutParams()메서드의 리턴값을ExecutionResult로 바꾸고 다양한 타입의 리턴값을 해당 클래스의 속성 중 ‘실제 데이터’(Object) 부분에 세팅했다.
1
2
3
4
5
public enum ResponseType {
HTML_PAGE,
DATA,
EMPTY
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
public ExecutionResult doRequestLogic(HttpRequest httpRequest, HttpResponse httpResponse) throws Exception {
HttpMethod httpMethod = httpRequest.getHttpMethod();
String requestUrl = httpRequest.getRequestUrl();
Map<String,String> params = httpRequest.getParams();
Execution execution = null;
switch (httpMethod) {
case GET:
execution = Optional.ofNullable(getMappingUrl.get(requestUrl)).orElseThrow(NoSuchMethodError::new);
break;
case POST:
execution = Optional.ofNullable(postMappingUrl.get(requestUrl)).orElseThrow(NoSuchMethodError::new);
break;
}
switch (execution.getResponseType()) {
case HTML_PAGE:
httpResponse.setStatusCode(HttpStatusCode3xx.REDIRECTION);
break;
case DATA:
httpResponse.setStatusCode(HttpStatusCode2xx.OK);
}
ExecutionResult result = (params!=null) ? executeMethodWithParams(execution, params, httpResponse) : executeMethodWithoutParams(execution, httpRequest);
return result;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
public class ExecutionResult {
private ResponseType responseType;
private Object returnData;
public ExecutionResult(ResponseType responseType, Object returnData) {
this.responseType = responseType;
this.returnData = returnData;
}
public ResponseType getResponseType() {
return responseType;
}
public Object getReturnData() {
return returnData;
}
}
LogicMapper에서 실행한 결과를 RequestHandler에서 받은 후 응답 타입에 따라 HTTP Response에 적절한 데이터 세팅해준다. 페이지 리다이렉트인 경우
httpResponse.setHeader("Location", redirectUrl);을 통해 헤더에Location : redirectUrl을 세팅해준다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
case REQUEST_BUSINESS_LOGIC:
ExecutionResult result = requestLogicMapper.doRequestLogic(httpRequest, httpResponse);
switch (result.getResponseType()) {
case HTML_PAGE:
String redirectPage = (String) result.getReturnData();
String redirectUrl = "http://localhost:8080"+redirectPage; // TODO : 하드코딩 말고 request origin으로 ?
httpResponse.setHeader("Location", redirectUrl);
break;
case DATA:
break;
case EMPTY:
httpResponse.setStatusCode(HttpStatusCode2xx.OK);
httpResponse.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/html;charset=utf-8");
httpResponse.setHeader("Content-Length", responseBody.length);
break;
}
구현하면서 알게된 것들
- HTTP Response 응답 헤더에
Location : url을 세팅하면 브라우저는 해당 url로 요청을 보낸다. - 상태코드
302 Found- 클라이언트가 요청한 리소스가 Location 헤더에 주어진 URL에 일시적으로 이동되었음을 가리킨다.
요구사항 5-1
- 로그인 메뉴를 클릭하면 해당 페이지로 이동한다. 로그인이 성공하면 /index.html로 이동하고, 실패하면 /user/login_failed.html로 이동해야 한다.
- 앞에서 회원가입한 사용자로 로그인할 수 있어야 한다.
구현하기 전 들었던 생각들
- 비즈니스 로직 수행하는 메서드들의 파라미터는 개수도 다양하고 타입도 다양한데 LogicMapper에 추상화 시킨 두 개의 메서드
executeMethodWithParams(),executeMethodWithoutParams()에서 어떻게 받아서 처리해야할까?- RequestHandler에서 LogicMapper로 넘어오는 파라미터의 형태는 Map인데, LogicMapper에서 맵핑시켜줄 다양한 비즈니스 로직 메서드의 파라미터를 일일이 맞추려면 추상화된 두 개의 메서드만 갖고는 불가능하다고 생각했다.
- 왜 이렇게 됐을까를 생각해보니 LogicMapper 입장에서 실제로 실행되는 비즈니스 로직 클래스, 파라미터 타입, 개수 등 알아야할게 너무 많은 것 같았다.
- 요구사항 2에 보면 LogicMapper의 미흡함에 대해 적어놨는데, 그 때 더 깊게 생각하지 않았던게 결국 발목을 잡은 것 같다.
구현
LogicMapper 개선 (RequestLogicMapper)
- LogicMapper에서 실제 비즈니스 로직을 바로 실행하는게 아니라, 중간에 LogicExecutor라는 객체를 둔다.
- LogicMapper에서는 들어온 요청에 따라 실제 로직 메서드가 아닌 LogicExecutor의 특정 메서드를 실행하고 파라미터도 Map 형태로만 넘기도록 수정.
- 하지만, 로직에서 추가적으로 필요한 파라미터로 HttpRequest, HttpResponse 등도 있을 수 있으므로 일단은 아래 코드처럼 Map, HttpRequest, HttpResponse했는데 해당 파라미터가 필요하지 않더라 받아야하므로 비효율적이다.
- 실제 Spring MVC에서는 Controller 단에서 HttpServletRequest, HttpServletRespone 등을 자유롭게 받을 수 있던데, 어떻게 가능한건지 공부해보자.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
public class RequestLogicMapper {
static class Execution {
private String methodName;
private ResponseType responseType;
public Execution(String methodName, ResponseType responseType) {
this.methodName = methodName;
this.responseType = responseType;
}
public String getMethodName() {
return methodName;
}
public ResponseType getResponseType() {
return responseType;
}
}
private LogicExecutor logicExecutor = LogicExecutor.getInstance();
private static Map<String, Execution> getMappingUrl = new HashMap<>();
private static Map<String, Execution> postMappingUrl = new HashMap<>();
static {
initGetRequest();
initPostRequest();
}
private static void initGetRequest() {
getMappingUrl.put("/user/create", new Execution("signup", ResponseType.HTML_PAGE));
getMappingUrl.put("/user/list", new Execution("getUserList", ResponseType.HTML_PAGE));
}
private static void initPostRequest() {
postMappingUrl.put("/user/create", new Execution("signup", ResponseType.HTML_PAGE));
postMappingUrl.put("/user/login", new Execution("login", ResponseType.HTML_PAGE));
}
public ExecutionResult doRequestLogic(HttpRequest httpRequest, HttpResponse httpResponse) throws Exception {
HttpMethod httpMethod = httpRequest.getHttpMethod();
String requestUrl = httpRequest.getRequestUrl();
Execution execution = null;
switch (httpMethod) {
case GET:
execution = Optional.ofNullable(getMappingUrl.get(requestUrl)).orElseThrow(NoSuchMethodError::new);
break;
case POST:
execution = Optional.ofNullable(postMappingUrl.get(requestUrl)).orElseThrow(NoSuchMethodError::new);
break;
}
switch (execution.getResponseType()) {
case HTML_PAGE:
httpResponse.setStatusCode(HttpStatusCode3xx.Found);
break;
case DATA:
httpResponse.setStatusCode(HttpStatusCode2xx.OK);
}
Map<String, String> params = httpRequest.getParams();
ExecutionResult result = (params != null) ? executeMethodWithParams(execution, params, httpRequest, httpResponse) : executeMethodWithoutParams(execution, httpRequest, httpResponse);
return result;
}
public ExecutionResult executeMethodWithParams(Execution execution, Map<String, String> params, HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response) throws Exception {
Method logic = logicExecutor.getClass().getMethod(execution.getMethodName(), Map.class, HttpRequest.class, HttpResponse.class);
Object returnObj = logic.invoke(logicExecutor, params, request, response);
return new ExecutionResult(execution.getResponseType(), returnObj);
}
public ExecutionResult executeMethodWithoutParams(Execution execution, HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response) throws Exception {
Method logic = logicExecutor.getClass().getMethod(execution.getMethodName(), HttpRequest.class, HttpResponse.class);
Object returnObj = logic.invoke(logicExecutor, request, response);;
return new ExecutionResult(execution.getResponseType(), returnObj);
}
}
LogicExecutor 구현
- LogicExcecutor에서는 Map형태로 받은 파라미터를 가공하여 실제 로직 메서드에 필요한 파라미터 형태로 만들고 해당 메서드를 호출한다.
- 이렇게 하고 보니 LogicExecutor가 MVC 모델에서 Controller와 약간 비슷한 역할이지 않나 하는 생각이 든다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
public class LogicExecutor {
private static final LogicExecutor logicExecutor = new LogicExecutor();
private LogicExecutor(){}
public static LogicExecutor getInstance() {
return logicExecutor;
}
private UserLogic userLogic = UserLogic.getInstance();
public String signup(Map<String, String> params, HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response) {
String id = params.get("userId");
String pw = params.get("password");
String name = params.get("name");
String email = params.get("email");
User newUser = new User(id, pw, name, email);
return userLogic.signup(newUser);
}
public String login(Map<String, String> params, HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response) {
String id = params.get("userId");
String pw = params.get("password");
return userLogic.login(id,pw,response);
}
}
요구사항 5-2
- 로그인이 성공하면 로그인 상태를 유지할 수 있어야 한다.
- 즉, 로그인이 성공할 경우 요청 헤더의 Cookie 헤더 값이
logined = true. 로그인이 실패하면logined = false로 전달되어야 한다.
구현
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
public String login(String id, String pw, HttpResponse response) throws IOException {
User findUser = findUser(id);
if(findUser!=null && pw.equals(findUser.getPassword())) {
response.setCookie("logined=true; Path=/");
return "/index.html";
}
response.setCookie("logined=false; Path=/");
return "/user/login_failed.html";
}
구현하면서 알게된 것들
- Set-Cookie 헤더의 속성 중 Path값을 따로 설정하지 않으면 쿠키를 응답한 화면이 포함된 디렉토리와 그 하위 디렉토리로 요청하는 경우에만 쿠키를 송신한다. (참고)
요구사항 6
접근하고 있는 사용자가 “로그인” 상태일 경우(Cookie로 판별) 사용자 리스트 페이지로 접근했을 때 사용자 목록을 출력한다. 만약 로그인하지 않은 상태라면 로그인 페이지로 이동한다.
구현
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public String getUserList(HttpRequest request) {
String isLogined = request.getCookie("logined");
if(isLogined!=null && isLogined.equals("true")) {
return "/user/list.html";
}
return "/user/login.html";
}
요구사항7
“CSS 지원하기”
구현하기 전 들었던 생각들
- 초반에 요청할 때 css 파일도 요청하고 응답받는데 왜 css 파일이 적용이 안된 화면이 렌더링될까 ?
구현
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
case REQUEST_STATIC_RESOURCE:
String requestUrl = httpRequest.getRequestUrl();
responseBody = (requestUrl.equals("/")) ? IOUtils.convertFileToByte(indexPage) : IOUtils.convertFileToByte(requestUrl);
String contentType = "text/html;charset=utf-8";
if(requestUrl.contains(".css")) {
contentType = "text/css";
} else if(requestUrl.contains(".js")) {
contentType = "application/javascript";
}
httpResponse.setStatusCode(HttpStatusCode2xx.OK);
httpResponse.setHeader("Content-Type", contentType);
httpResponse.setHeader("Content-Length", responseBody.length);
break;
구현하면서 알게된 것들
- 브라우저가 css 파일을 읽고 적용하기 위해선
Content-type을"text/css"로 세팅해줘야 한다 - js 파일은
Content-type"application/javascript"로 세팅해줘야한다.
정리
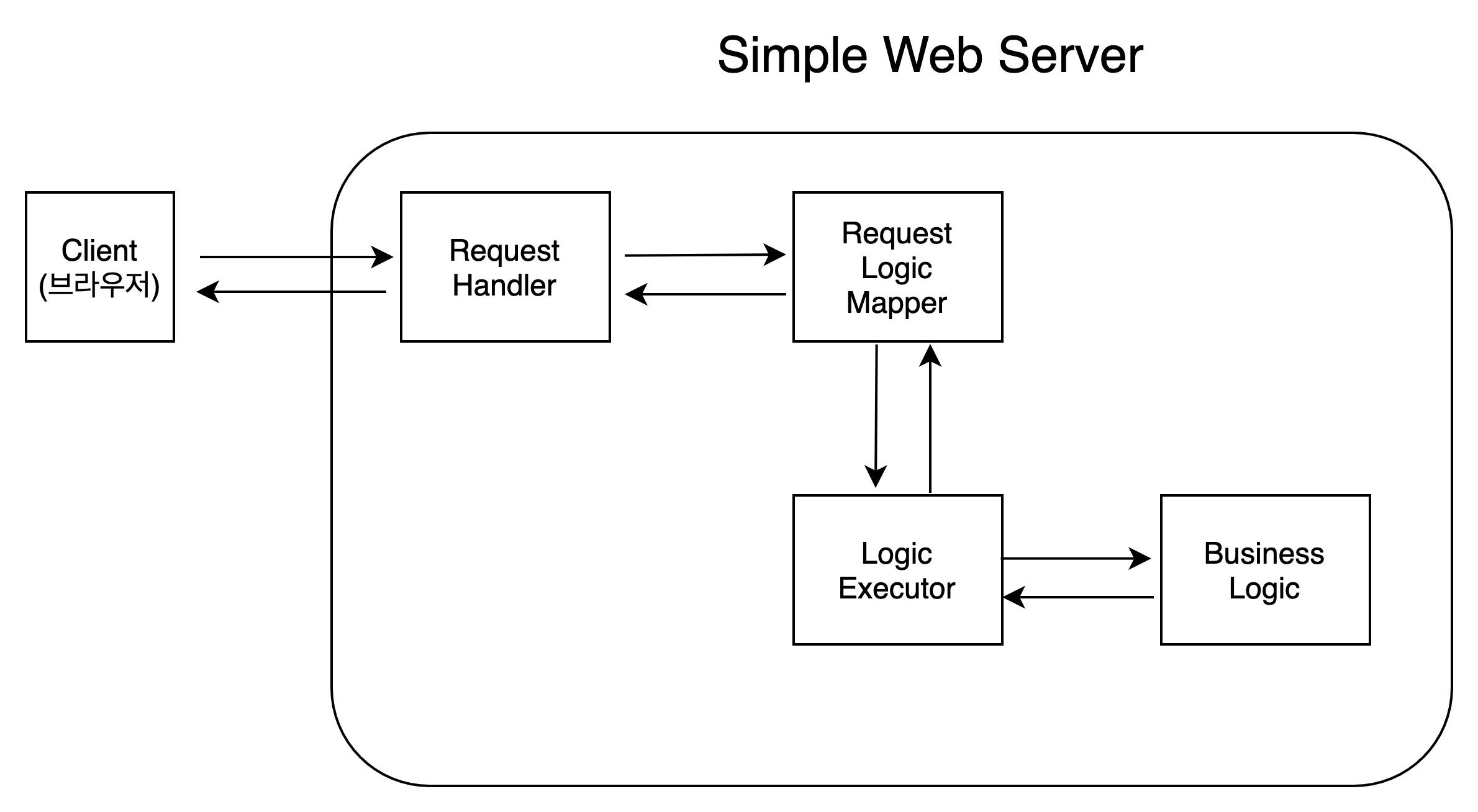
- 구현한 웹 서버를 도식화 해보면 아래와 같다.
- 요구사항 5~6에서 파라미터를 원하는 것만 받게 하려면 어떻게 해야할지는 좀 더 공부해보자.

- 요구사항 5~6에서 파라미터를 원하는 것만 받게 하려면 어떻게 해야할지는 좀 더 공부해보자.