들어가기 전 글을 작성하는 현재(21.09.25) 자바 최신버전은 JDK17이다. 각 버전별 특징을 살펴보면서 이런게 있구나 정도를 인지하고, 추후에 공부가 필요한 부분은 좀 더 상세히 공부해보자.
History 9 버전부터는 6개월 단위로 새로운 버전이 출시되고 있다.
버전 출시일 JDK 1.0 1996년 1월 JDK 1.1 1997년 2월 J2SE 1.2 1998년 12월 J2SE 1.3 2000년 5월 J2SE 1.4 2002년 2월 J2SE 5.0 2004년 9월 Java SE 6 2006년 12월 Java SE 7 (LTS) 2011년 7월 Java SE 8 (LTS) 2014년 3월 Java SE 9 2017년 9월 Java SE 10 2018년 3월 Java SE 11 (LTS) 2018년 9월 Java SE 12 2019년 3월 Java SE 13 2019년 9월 Java SE 14 2020년 3월 Java SE 15 2020년 9월 Java SE 16 2021년 3월 Java SE 17 (LTS) 2021년 9월 Java SE 18 (예정) 2022년 3월 Java SE 19 (예정) 2022년 9월 Java SE 20 (예정) 2023년 3월 Java SE 21 (예정, LTS) 2023년 9월
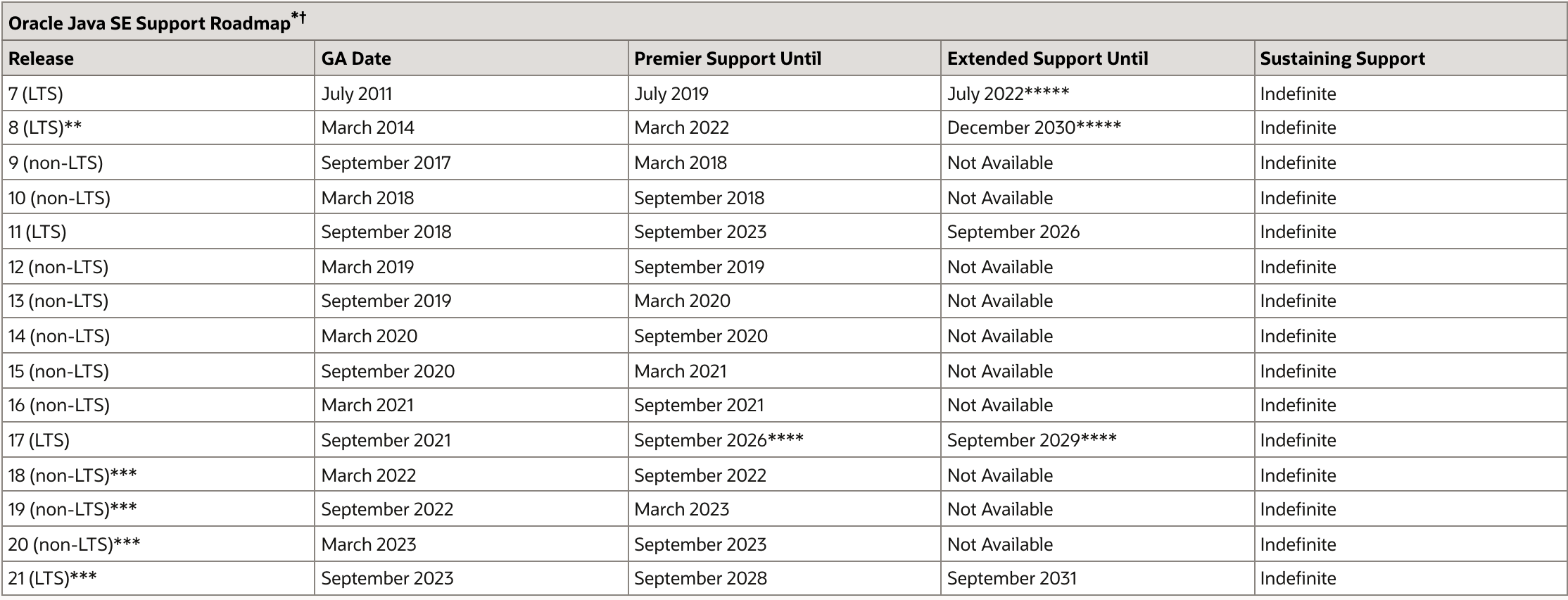
LTS (Long Term Support) Oracle은 Oracle Lifetime 지원 정책 에 설명된 대로 Oracle Java SE 제품에 대한 Oracle Premier Support를 고객에게 제공한다. Java SE 8 이후의 제품 릴리스의 경우 Oracle은 특정 릴리스만 LTS(Long-Term-Support) 릴리스로 지정한다.Java SE 7, 8, 11 및 17은 LTS 릴리스이다. 오라클은 향후 2년마다 LTS를 출시할 계획이며, 이는 다음 LTS 출시가 2023년 9월에 Java 21이라는 것을 의미한다. Oracle Premier Support를 위해, non-LTS 릴리스는 최신 LTS 릴리스의 구현 개선 사항의 누적 집합으로 간주된다. 새로운 기능 릴리스가 제공되면, 이전의 non-LTS 릴리스는 대체된 것으로 간주된다.예를 들어 Java SE 9는 non-LTS 릴리스였으며 즉시 Java SE 10(non-LTS)으로 대체되었다. Java SE 10은 즉시 Java SE 11로 대체되었다. Java SE 11은 LTS 릴리스이므로 Oracle 고객은 Java SE 12가 릴리스되었더라도 Oracle Premier Support 및 정기 업데이트를 받게 된다. 출처 : https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/java-se-support-roadmap.html
이제 자바의 버전별 특징을 간략하게 살펴보자. 아직 공식적으로 지원하는 버전인 7부터 정리해보았다.
Java 7 String in switch statement before java 71
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
public void testStringInSwitch ( String param ){
final String JAVA5 = "Java 5" ;
final String JAVA6 = "Java 6" ;
final String JAVA7 = "Java 7" ;
if ( param . equals ( JAVA5 )){
System . out . println ( JAVA5 );
} else if ( param . equals ( JAVA6 )){
System . out . println ( JAVA6 );
} else if ( param . equals ( JAVA7 )){
System . out . println ( JAVA7 );
}
}
from java 71
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
public void testStringInSwitch ( String param ){
final String JAVA5 = "Java 5" ;
final String JAVA6 = "Java 6" ;
final String JAVA7 = "Java 7" ;
switch ( param ) {
case JAVA5:
System . out . println ( JAVA5 );
break ;
case JAVA6:
System . out . println ( JAVA6 );
break ;
case JAVA7:
System . out . println ( JAVA7 );
break ;
}
}
Binary Literals before java 71
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
public void testBinaryIntegralLiterals (){
int binary = 8 ;
if ( binary == 8 ){
System . out . println ( true );
} else {
System . out . println ( false );
}
}
from java 71
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
public void testBinaryIntegralLiterals (){
int binary = 0b1000 ; //2^3 = 8
if ( binary == 8 ){
System . out . println ( true );
} else {
System . out . println ( false );
}
}
The try-with-resources before java 71
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
public void testTryWithResourcesStatement () throws FileNotFoundException , IOException {
FileInputStream in = null ;
try {
in = new FileInputStream ( "java7.txt" );
System . out . println ( in . read ());
} finally {
if ( in != null ) {
in . close ();
}
}
}
from java 71
2
3
4
5
6
public void testTryWithResourcesStatement () throws FileNotFoundException , IOException {
try ( FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream ( "java7.txt" )) {
System . out . println ( in . read ());
}
}
Multi-Catch Similar Exceptions before java 71
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public void testMultiCatch (){
try {
throw new FileNotFoundException ( "FileNotFoundException" );
} catch ( FileNotFoundException fnfo ) {
fnfo . printStackTrace ();
} catch ( IOException ioe ) {
ioe . printStackTrace ();
}
from java 71
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
public void testMultiCatch (){
try {
throw new FileNotFoundException ( "FileNotFoundException" );
} catch ( FileNotFoundException | IOException fnfo ) {
fnfo . printStackTrace ();
}
}
Underscores in Numeric Literals 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
public void testUnderscoresNumericLiterals () {
int oneMillion_ = 1_000_000 ; //new
int oneMillion = 1000000 ;
if ( oneMillion_ == oneMillion ){
System . out . println ( true );
} else {
System . out . println ( false );
}
}
Java 8 Interface Default and Static Methods Java 8 이전에는 인터페이스에 public 추상 메서드만 선언할 수 있었다. Java 8 부터는 static, default 메서드를 선언할 수 있다.
static method정적 메서드는 인터페이스 내부에서만 사용할 수 있으며,. 구현 클래스에서 재정의할 수 없다. 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public interface Vehicle {
static String producer () {
return "N&F Vehicles" ;
}
}
String producer = Vehicle . producer ();
default methoddefault 메소드는 default 키워드를 사용하여 선언된다. 해당 메서드는 구현 클래스의 인스턴스를 통해 액세스할 수 있다. 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public interface Vehicle {
default String getOverview () {
return "ATV made by " + producer ();
}
}
public class VehicleImpl implements Vehicle {
...
}
Vehicle vehicle = new VehicleImpl ();
String overview = vehicle . getOverview ();
Optional Java 8 이전에는 NPE(NullPointerException)가 발생할 가능성 때문에 개발자가 참조한 값의 유효성을 주의 깊게 확인해야 했다. 유효성 검사를 위해 성가시고 오류가 발생하기 쉬운 boilerplate code가 필요했다. Optional<T> 클래스는 T 타입의 객체에 대한 컨테이너로 작동한다. 이 값이 null이 아닌 경우 이 객체의 값을 반환할 수 있다. 이 컨테이너 내부의 값이 null이면 NPE를 던지는 대신 미리 정의된 일부 작업을 수행할 수 있다.
1
2
List < String > list = getList ();
List < String > listOpt = list != null ? list : new ArrayList <>();
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
User user = getUser ();
if ( user != null ) {
Address address = user . getAddress ();
if ( address != null ) {
String street = address . getStreet ();
if ( street != null ) {
return street ;
}
}
}
return "not specified" ;
1
List < String > listOpt = getList (). orElseGet (() -> new ArrayList <>());
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Optional < User > user = Optional . ofNullable ( getUser ());
String result = user
. map ( User: : getAddress )
. map ( Address: : getStreet )
. orElse ( "not specified" );
Optional < OptionalUser > optionalUser = Optional . ofNullable ( getOptionalUser ());
String result = optionalUser
. flatMap ( OptionalUser: : getAddress )
. flatMap ( OptionalAddress: : getStreet )
. orElse ( "not specified" );
Lambda 표현식 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
// 익명 내부 클래스 사용
Runnable runnable = new Runnable (){
@Override
public void run (){
System . out . println ( "Hello world !" );
}
};
// 람다 사용
Runnable runnable = () -> System . out . println ( "Hello world two!" );
Collections & Streams Stream API 활용하여 함수형 프로그래밍 스타일로 코딩 가능
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
List < String > list = Arrays . asList ( "franz" , "ferdinand" , "fiel" , "vom" , "pferd" );
list . stream ()
. filter ( name -> name . startsWith ( "f" ))
. map ( String: : toUpperCase )
. sorted ()
. forEach ( System . out :: println );
Java 9 Collections List, Set, Map을 쉽게 생성할 수 있는 헬퍼 메서드가 생겼다.
1
2
3
List < String > list = List . of ( "one" , "two" , "three" );
Set < String > set = Set . of ( "one" , "two" , "three" );
Map < String , String > map = Map . of ( "foo" , "one" , "bar" , "two" );
Streams takeWhile, dropWhile, iterate 메서드가 추가되었다.
1
2
Stream < String > stream = Stream . iterate ( "" , s -> s + "s" )
. takeWhile ( s -> s . length () < 10 );
Optionals ifPresentOrElse 메서드가 추가되었다.
1
user . ifPresentOrElse ( this :: displayAccount , this :: displayLogin );
Interfaces 인터페이스 내에서 private 메서드를 선언할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
public interface MyInterface {
private static void myPrivateMethod (){
System . out . println ( "Yay, I am private!" );
}
}
HttpClient (Preview) Java 9는 자체적인 최신 Http 클라이언트인 HttpClient Preview 버전을 도입했다. 이 전까지의 Java의 내장 Http 지원은 다소 낮은 수준이었고 Apache HttpClient 또는 OkHttp와 같은 타사 라이브러리를 사용해야 했다. Java 10 var 키워드 지역 변수(메서드 내 변수)에 대해 타입 추론이 가능하다.
1
2
3
public void foo () {
var name = "Lee" ;
}
Java 11 Java 10은 라이선스 없이 상업적으로 사용할 수 있는 마지막 무료 Oracle JDK 릴리스였다. 즉, Java 11부터는 LTS를 사용하려면 비용을 지불해야 한다.
Strings & Files String, Files 클래스에 새로운 메서드가 추가됐다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
"Marco" . isBlank ();
"Mar\nco" . lines ();
"Marco " . strip ();
Path path = Files . writeString ( Files . createTempFile ( "helloworld" , ".txt" ), "Hi, my name is!" );
String s = Files . readString ( path );
Running Java Files 자바 파일을 실행하기 위해 javac로 컴파일 하지 않아도 된다.
before java 111
2
3
$ javac HelloWorld.java
$ java HelloWorld
Hello Java 8!
from java 111
2
$ java HelloWorld.java
Hello Java 11!
람다식에 var 키워드 사용 1
( var firstName , var lastName ) -> firstName + lastName
Not Predicate Method Predicate 인터페이스에 정적 not() 메소드가 추가되었다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
List < String > sampleList = Arrays . asList ( "Java" , "\n \n" , "Kotlin" , " " );
List withoutBlanks = sampleList . stream ()
. filter ( Predicate . not ( String: : isBlank ))
. collect ( Collectors . toList ());
assertThat ( withoutBlanks ). containsExactly ( "Java" , "Kotlin" );
HttpClient (Standard) 새로운 HTTP API는 전반적인 성능을 향상시키고 HTTP/1.1 및 HTTP/2를 모두 지원한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
HttpClient httpClient = HttpClient . newBuilder ()
. version ( HttpClient . Version . HTTP_2 )
. connectTimeout ( Duration . ofSeconds ( 20 ))
. build ();
HttpRequest httpRequest = HttpRequest . newBuilder ()
. GET ()
. uri ( URI . create ( "http://localhost:" + port ))
. build ();
HttpResponse httpResponse = httpClient . send ( httpRequest , HttpResponse . BodyHandlers . ofString ());
assertThat ( httpResponse . body ()). isEqualTo ( "Hello from the server!" );
Collections java.util.Collection 인터페이스에는 IntFunction 인수를 사용하는 새로운 기본 toArray() 메소드가 포함된다. 이렇게 하면 컬렉션에서 배열을 더 쉽게 생성할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
List sampleList = Arrays . asList ( "Java" , "Kotlin" );
String [] sampleArray = sampleList . toArray ( String []:: new );
assertThat ( sampleArray ). containsExactly ( "Java" , "Kotlin" );
Java 12 Switch Expression(Preview) 1
2
3
4
5
boolean result = switch ( status ) {
case SUBSCRIBER -> true ;
case FREE_TRIAL -> false ;
default -> throw new IllegalArgumentException ( "something is murky!" );
};
Java 13 Multiline Strings (Preview) 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
String htmlWithJava13 = """
<html>
<body>
<p>Hello, world</p>
</body>
</html>
""" ;
Java 14 Switch Expression (Standard) 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
int numLetters = switch ( day ) {
case MONDAY , FRIDAY , SUNDAY -> 6 ;
case TUESDAY -> 7 ;
default -> {
String s = day . toString ();
int result = s . length ();
yield result ;
}
};
Records (Preview) boilerplate code를 작성하는 고통을 완화하는 데 도움이 되는 Record 클래스가 추가되었다. 해당 클래스는 데이터,(잠재적으로) getter/setter, equals/hashcode, toString만 포함된다.
before1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
final class Point {
public final int x ;
public final int y ;
public Point ( int x , int y ) {
this . x = x ;
this . y = y ;
}
}
// state-based implementations of equals, hashCode, toString
// nothing else
record 사용 1
2
3
4
5
public record Point ( int x , int y ) { }
var point = new Point ( 1 , 2 );
point . x (); // returns 1
point . y (); // returns 2
Helpful NullPointerException 마침내 NullPointerException은 정확히 어떤 변수가 null인지 설명한다.
1
2
3
4
author . age = 35 ;
---
Exception in thread "main" java . lang . NullPointerException :
Cannot assign field "age" because "author" is null
Pattern Matching For InstanceOf (Preview) instanceof로 타입 검사 후 형변환을 할 필요가 없어졌다.
1
2
3
if ( obj instanceof String s ) {
System . out . println ( s . contains ( "hello" ));
}
필요한 모든 종속성을 포함하여 Java 애플리케이션을 플랫폼별 패키지로 패키징할 수 있는 인큐베이팅 패키지 도구가 도입됐다.
Linux: deb and rpm macOS: pkg and dmg Windows: msi and exe Garbage Collectors Concurrent Mark Sweep(CMS) Garbage Collector가 제거되고 실험용 Z Garbage Collector가 추가되었다. Java 15 Text-Blocks / Multiline Strings Java 13의 실험 기능으로 도입된 Multiline Strings은 이제 production-ready 단계가 되었다.
1
2
3
4
5
String text = """
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing \
elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore \
et dolore magna aliqua.\
""" ;
Sealed Classes (Preview) 이것은 클래스가 public인 동안 Shape을 서브클래스로 허용하는 유일한 클래스는 Circle, Rectangle 및 Square임을 의미한다. 1
2
public abstract sealed class Shape
permits Circle , Rectangle , Square {...}
ZGC: Production Ready Z Garbage Collector는 더 이상 실험용이 아닌 production-ready 단계가 되었다. Java 16 Unix-Domain Socket Channels 이제 Unix 도메인 소켓에 연결할 수 있습니다(macOS 및 Windows(10+)에서도 지원됨).
1
2
socket . connect ( UnixDomainSocketAddress . of (
"/var/run/postgresql/.s.PGSQL.5432" ));
Foreign Linker API (Preview) JNI(Java Native Interface)에 대한 계획된 교체로, 기본 라이브러리에 바인딩할 수 있다. Records & Pattern Matching Records 클래스 및 Pattern Matching 모두 production-ready 단계가 되었다. Java 17 Sealed Class (Standard) 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public abstract sealed class Shape
permits Circle , Rectangle {...}
public class Circle extends Shape {...} // OK
public class Rectangle extends Shape {...} // OK
public class Triangle extends Shape {...} // Compile error
// No need for default case if all permitted types are covered
double area = switch ( shape ) {
case Circle c -> Math . pow ( c . radius (), 2 ) * Math . PI
case Rectangle r -> r . a () * r . b ()
};
Pattern Matching For switch (Preview) 1
2
3
4
5
6
String formatted = switch ( o ) {
case Integer i && i > 10 -> String . format ( "a large Integer %d" , i );
case Integer i -> String . format ( "a small Integer %d" , i );
case Long l -> String . format ( "a Long %d" , l );
default -> o . toString ();
};
참고 자료