상황
- ‘자바 웹 프로그래밍 NextStep’ 3장의 과제 중 하나인 웹 서버를 구현하기 위해 HTTP 요청이 서버에 어떤식으로 들어오는지를 보고싶었다.
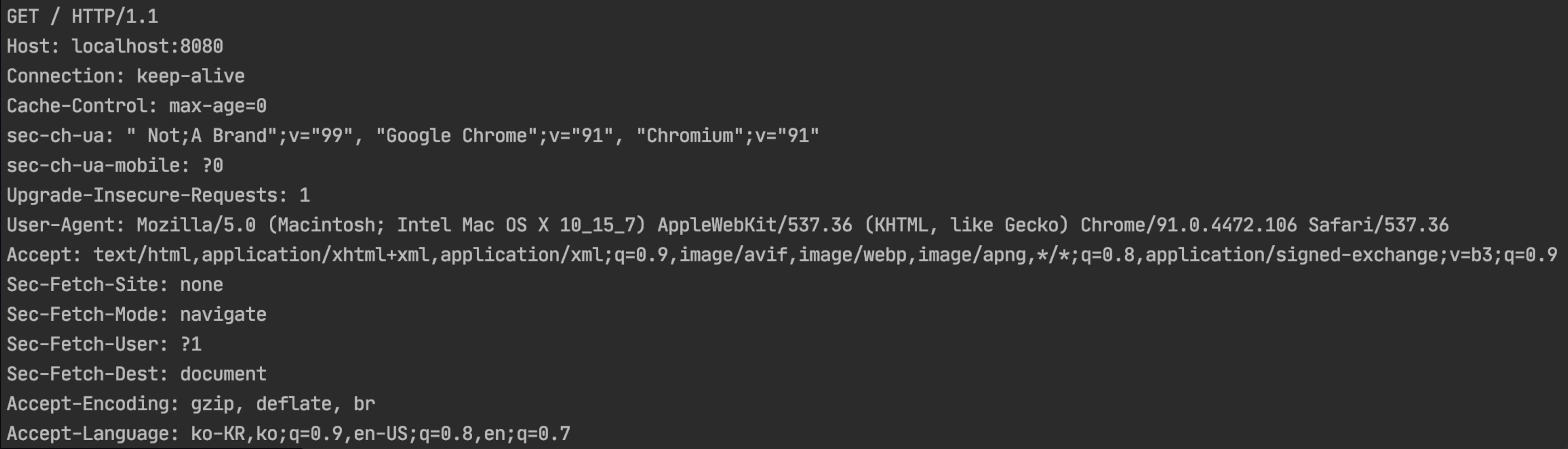
- 따라서, 단순 확인을 위해 다음과 같은 코드를 작성하여 실행시키고 브라우저에서 localhost:8080 으로 요청을 보냈다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23
public class TestServer { public void start() throws IOException { ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8080); Socket connection; while((connection = serverSocket.accept()) !=null) { System.out.println(String.format("[connection info]%nIpAddr : %s, Port : %s%n", connection.getInetAddress(), connection.getPort())); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(connection.getInputStream())); String line; while((line=br.readLine())!=null) { // 여기서 멈춘다 System.out.println(line); } System.out.println("END!"); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { TestServer server = new TestServer(); server.start(); } }
아래와 같이 요청이 들어오는 것을 확인할 수 있었고, ‘Http Method(GET, POST, …)가 뭔지 확인하려면 요청의 첫 번째 라인을 확인하면 되겠구나’ 등의 판단을 할 수 있었다.

- 하지만, 문제는 코드의 15번째 라인
System.out.println("END!");에 대한 출력이 콘솔에 찍히지 않았다는 것이었다. 디버거로 확인해보니 무한루프를 도는 것도 아니고 위 코드의 11번째 라인에서 대기 상태가 되는 것을 확인할 수 있었다.
해결 과정
스택오버플로우에 있는 글 을 통해 BufferedReader의 readLine() 메서드는 라인이 종료되었다고 판단되지 않으면 값을 리턴하지 않는다는 것을 알게되었다.
- 그렇다면 라인이 종료되었다는 것을 판단하는 기준은 뭘까??
- 자바 공식문서 에 나와있는 readLine() 메서드에 대한 설명을 보면 끝에 다음 문자(‘\n’, ‘\r’, ‘\r\n’) 중 하나가 있어야 하나의 라인으로 인식한다고 한다.
Reads a line of text. A line is considered to be terminated by any one of a line feed (‘\n’),
a carriage return (‘\r’), or a carriage return followed immediately by a linefeed.
- 자바 공식문서 에 나와있는 readLine() 메서드에 대한 설명을 보면 끝에 다음 문자(‘\n’, ‘\r’, ‘\r\n’) 중 하나가 있어야 하나의 라인으로 인식한다고 한다.
- 또한, BufferedReader의 readLine() 메서드를 직접 들여다보면 다음과 같은 로직이 있는 것을 확인할 수 있다. eol은 ‘end of line’이지 않을까 싶다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
charLoop: for (i = nextChar; i < nChars; i++) { c = cb[i]; if ((c == '\n') || (c == '\r')) { eol = true; break charLoop; } }
- 그렇다면, HTTP 요청의 마지막 라인이 어떻길래 아직 라인이 종료되었다고 판단하지 않는걸까 ?
- 스택오버플로우에 있는 글
- RFC 문서 34p
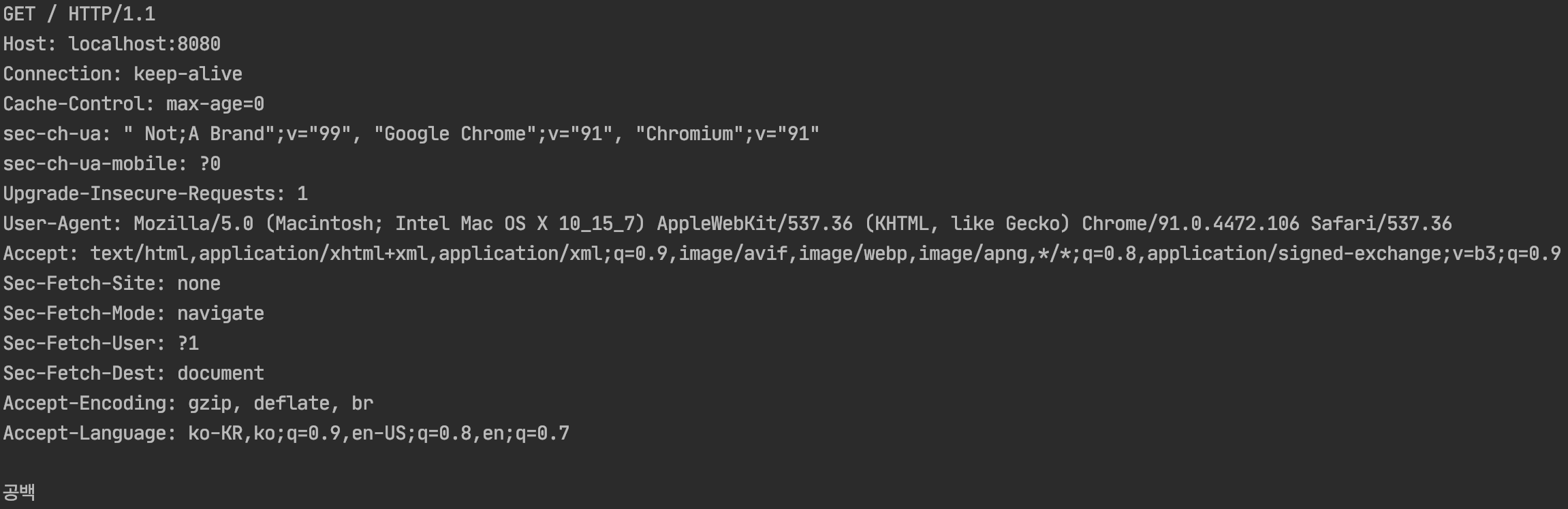
- HTTP 요청 형태 (HTTP 요청 헤더의 마지막 라인은 공백이었고 이로 인해 readLine() 메서드가 라인이 끝나지 않았다고 판단한 것)
- CRLF : Carriage Return(커서의 위치를 맨 앞으로 이동) + Line Feed(커서를 한 칸 아래로 이동)
1
2
3
4
5
6
Request-Line
*(( general-header
| request-header
| entity-header ) CRLF)
CRLF
[ message-body ]
- 결과적으로 line이 공백이면
"공백"이라는 문자열을 출력해봄으로써 실제 HTTP 요청이 위와 같이 들어온다는 것을 알 수 있었고, 공백인 경우 break를 통해 while문 내에서 계속 대기상태에 머물러있지 않게 할 수 있었다.
※ 참고. HTTP Response 포맷
1
2
3
4
5
6
Status-Line
*(( general-header
| response-header
| entity-header ) CRLF)
CRLF
[ message-body ]
요약
현상
- HTTP 요청을 받아서 BufferedReader의 readLine() 메서드로 읽어 올 때 특정 라인에 도달하면 대기 상태에 머문다.
원인
- readLine() 메서드 내에는 ‘하나의 라인’이라고 판단하는 기준(라인 마지막에 ‘\n’, ‘\r’, ‘\r\n’)이 있는데,
HTTP 요청의 마지막 라인은 공백이었기 때문에 아직 한 라인이 끝나지 않았다고 판단하여 계속 대기하고 있었다.
배운 것
- HTTP 요청 형태
- BufferedReader의 readLine() 메서드가 라인을 인식하는 방법
실제 코드 적용
- 간단한 웹 서버 구현 레파지토리
- 오늘 내용 관련 코드
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54
private static HttpRequest processGetRequest(String requestUrl, BufferedReader bufferedReader) throws IOException { Map<String, String> cookies = null; for (String line = bufferedReader.readLine(); (line != null && !line.isEmpty()); line = bufferedReader.readLine()) { if (line.contains("Cookie")) { String[] info = line.split(":"); cookies = parseCookies(info[1]); break; } } if (!requestUrl.contains("?")) { return new HttpRequest(HttpMethod.GET, requestUrl, cookies); } String[] info = requestUrl.split("\\?"); Map<String, String> params = parseQueryString(info[1]); return new HttpRequest(HttpMethod.GET, info[0], params, cookies); } private static HttpRequest processPostRequest(String requestUrl, BufferedReader bufferedReader) throws IOException { int contentLen = 0; String contentType = ""; Map<String, String> params = null; Map<String, String> cookies = null; for (String line = bufferedReader.readLine(); (line != null && !line.isEmpty()); line = bufferedReader.readLine()) { if (line.contains("Content-Length")) { String[] info = line.split(":"); contentLen = Integer.parseInt(info[1].trim()); } else if (line.contains("Content-Type")) { String[] info = line.split(":"); contentType = info[1].trim(); // ex) application/x-www-form-urlencoded } else if (line.contains("Cookie")) { String[] info = line.split(":"); cookies = parseCookies(info[1]); } } if (contentLen > 0) { char[] body = new char[contentLen]; bufferedReader.read(body); if (contentType.equals("application/x-www-form-urlencoded")) { String queryString = new String(body); params = parseQueryString(queryString); } else if (contentType.equals("application/json")) { // TODO } } return new HttpRequest(HttpMethod.POST, requestUrl, params, cookies); }
더 공부해야할 부분
- JAVA I/O
- HTTP 응답 분할(HTTP Response Splitting, CRLF) 취약점